

Since the proton is much more massive than the electron, we will assume throughout this chapter that the reduced mass equals the electron mass and the proton is located at the center of mass. Schrdinger's Wave Equation (Derivation) Considering a complex plane wave: Now the Hamiltonian of a system is : Here ‘V’ is the potential energy and ‘T’ is the kinetic energy. The length of \(r\) is the distance between the proton and the electron, and the direction of \(r\) and the direction of \(r\) is given by the orientation of the vector pointing from the proton to the electron. Finally, the difference between the classical wave equation and the quantum Schrdinger one is explained in order to help the students to grasp the meaning of. Erwin Schrodinger (1887-1961) was a titan of theoretical physics who died exactly 60 years ago, leaving behind an equation named after him that has become a pillar of quantum mechanics, the branch of physics that studies the behavior of particles (including light) at the sub-atomic level. In this chapter we investigate solutions of Schrdingers wave equation and apply these to a.

Therefore option 1 is incorrect and 2 is correct.
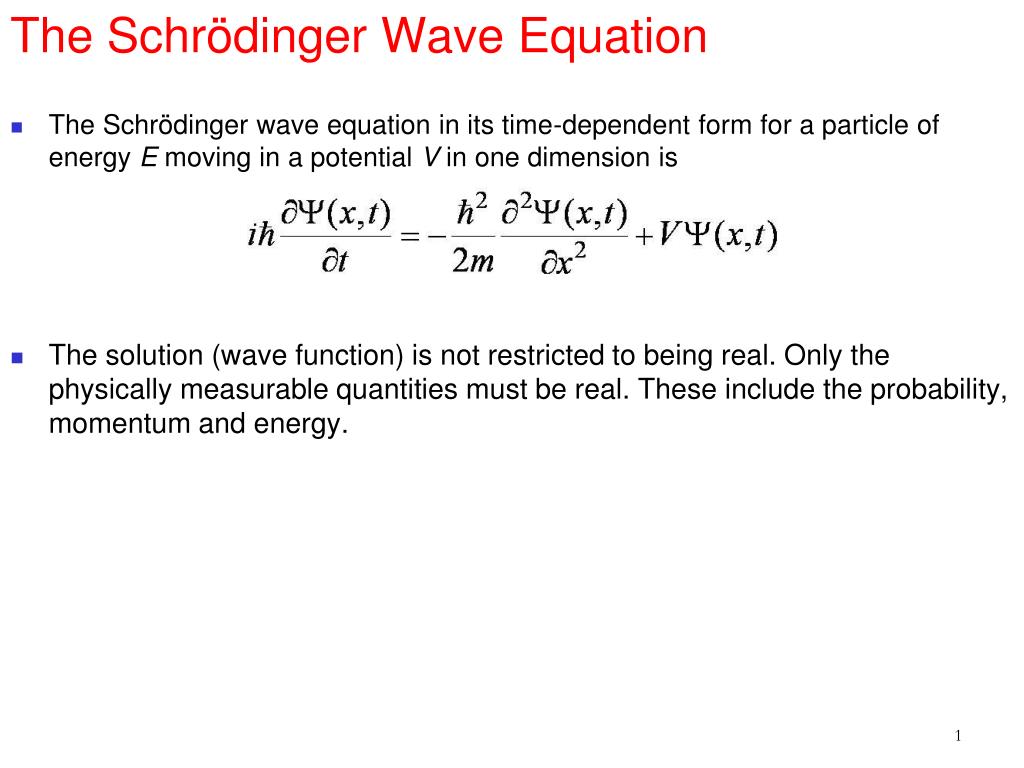
From the above, it is clear that the Schrdinger equation is a linear partial differential equation. This reduced particle is located at \(r\), where \(r\) is the vector specifying the position of the electron relative to the position of the proton. The Schrdinger equation (also known as Schrdinger’s wave equation) is a partial differential equation that describes the dynamics of quantum mechanical systems via the wave function. The hydrogen atom, consisting of an electron and a proton, is a two-particle system, and the internal motion of two particles around their center of mass is equivalent to the motion of a single particle with a reduced mass.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
